CTP (Computer-to-Plate) plates for offset printing are advanced aluminum plates designed for high-quality image reproduction in printing. They are an essential part of the offset printing process, enabling precise and efficient image transfer.

| Specification | Details |
| Product Type | CTP Plate |
| Compatible Platesetter | All the dominant platesetters |
| Aluminum | Aluminum alloy 1050/1060 standard |
| Plate Thickness | 0.15/0.20/0.25/0.30/0.40 mm |
| Maximum Coil Width | 1350 mm |
| Spectral Sensitivity | 830 nm |
| Exposure Energy | 110-130 mJ/c㎡ |
| Developing Condition | 24-28℃, 25-35 seconds |
| Safe-light | 2 hours under white light |
| Resolution | 1-99% at 200 lpi |
| Run Length | 50, 000-100, 000 copies (Unbaked), 100, 000-200, 000 copies (Baked) *Run Length varies with printing conditions and content |
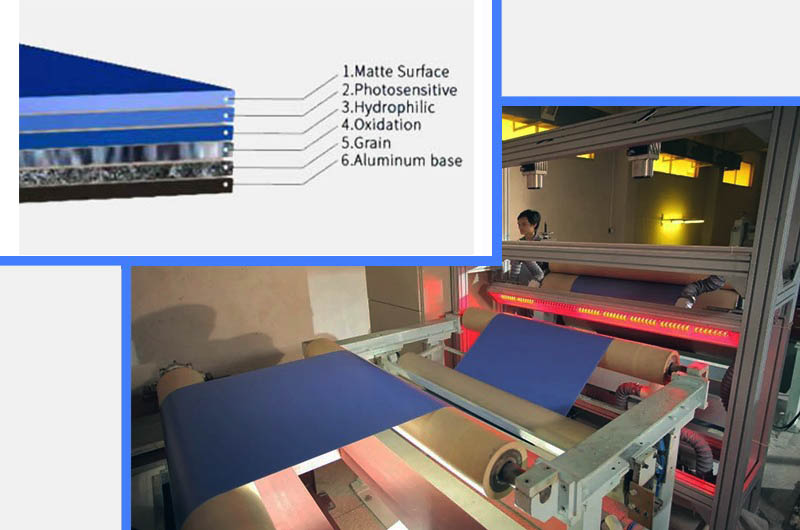
CTP plates are widely used in the printing of newspapers, magazines, packaging, and promotional materials, where quality and efficiency are essential.
Selecting the right Computer-to-Plate (CTP) technology is critical in the printing industry, with both thermal and violet CTP plates offering distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Thermal CTP plates, which rely on heat to form images, are prized for their high print quality and fast plate-making speeds. These plates respond to laser heat, allowing the exposed areas to become ink-receptive. While thermal plates are more costly and less environmentally friendly, they excel in quality and efficiency. HC Aluminum Co., Ltd offers two varieties of thermal plates:
| Characteristics | Single Layer Thermal CTP Plate | Double Layer Thermal CTP Plate |
| Description | This plate uses an advanced coating formula that is easy to use and offers reliable performance without preheating. | Designed with a double coating on a high-quality aluminum base, this plate provides UV resistance, high stability, and excellent dot reproduction. |
| Key Advantages | High dot reproducibility | Strong durability and printability, stable performance under demanding conditions |
| Excellent resolution | ||
| Optimized ink-water balance due to its oxide layer and hydrophilicity | ||
| Suitable Applications | Ideal for applications requiring high-quality images and fast plate-making | Suitable for applications requiring strong durability and stable performance |
| Preheating Requirement | No preheating required | (Depends on equipment and application) |
| Stability | Good stability | High stability, suitable for demanding printing environments |
| UV Resistance | Low | High UV resistance |
| Compatible Substrates | Suitable for various standard printing substrates | Suitable for substrates requiring durability and high-quality output |
This table allows you to clearly compare the characteristics and suitable applications of single-layer and double-layer thermal CTP plates, helping you choose the plate type that best meets your needs.
Violet plates, in contrast, use violet light, making them less costly and more environmentally friendly. However, they tend to be slower and offer slightly lower image quality than thermal plates. Violet plates can be suitable for businesses prioritizing environmental considerations and cost savings but might not achieve the same image clarity as thermal plates.
When choosing a suitable CTP plate, it’s essential to consider factors like print volume, plate type, image quality, substrate type, plate size, budget, and environmental impact to ensure that the selected plate meets printing requirements and aligns with budget and environmental goals.
| Key Factor | Description |
| Print Volume | Print volume directly determines the durability required for the plate. High-volume printing requires more durable plates to withstand longer print cycles and higher print loads. For long-run printing, durable thermal or violet plates are typically chosen to ensure stable print quality throughout the process. |
| Plate Type | The type of plate should be based on printing speed and plate-making efficiency needs. Thermal plates excel in fast plate-making and high-quality image details, ideal for users prioritizing speed and precision. Violet plates are more cost-effective, suitable for print projects where cost control is important. Equipment compatibility and plate processing steps should be considered; thermal plates are often suited to highly automated equipment. |
| Image Quality | Image quality requirements directly impact the choice of plate type. If the project requires fine image detail and high-quality output, thermal plates are preferable due to their superior resolution and ability to capture precise dots and image details. For standard-quality print projects, violet plates offer an economical option that meets general printing needs. |
| Substrate Type | The type of printing substrate used also affects plate selection. For non-porous substrates (e.g., plastic, metal) or special substrate needs, thermal plates are more suitable, as they provide higher adhesion and precise color reproduction on these materials. For paper and other standard substrates, violet or thermal plates can be chosen based on budget and desired print quality. |
| Plate Size | Plate size must match the specifications of the printing press. When selecting a plate, ensure the size is suitable for the printing equipment and production needs. Different types of plates (thermal, violet) may vary in size, so it’s important to ensure that the selected plate is compatible with your printing equipment to avoid waste and production delays. |
| Budget | Budget is a crucial factor in choosing a CTP plate. Plate costs depend on type, size, and print volume. While thermal plates are suited for high-quality printing, they are more expensive, whereas violet plates are more economical. For print jobs with limited budgets, violet plates may be more suitable. Select a plate type that meets needs and is cost-effective to help control printing costs. |
| Environmental Impact | For printing companies concerned with environmental impact, the plate’s effect on the environment is an important factor. Compared to thermal plates, violet plates consume less energy and produce fewer emissions during manufacturing, making them more environmentally friendly. Due to their eco-friendly advantages, violet plates are suitable for companies and projects aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and meet environmental standards. |
Both coated surfaces are placed facing each other with a neutral liner paper in between, covered externally with black kraft paper lined with plastic, and then packed into cartons with approximately 50-100 sheets per carton. The cartons are placed on wooden pallets, protected by wooden frames or cardboard. Finally, the pallets are wrapped with kraft paper or plastic film and secured with plastic tape. Custom packaging is also available upon request.
1. What is CTP in Offset Printing?
CTP, or Computer-to-Plate technology, is a digital imaging method used in offset printing where a digital file directly transfers onto a printing plate. Unlike traditional methods that involve film-based transfers, CTP improves speed, image quality, and reduces manual steps, enhancing precision in print production.
2. What is the Difference Between CTP and CTCP Plates?
| Feature | CTP (Computer-to-Plate) | CTCP (Computer-to-Conventional Plate) |
| Exposure Method | Directly uses a laser system | Uses a UV laser system to expose traditional offset plates |
| Resolution | High, suitable for high-quality offset printing | Lower, suitable for certain applications, but with lower quality and durability |
| Cost | Higher | More cost-effective |
| Application Scenarios | High-quality printing needs, such as art printing and high-end publishing | Suitable for medium to low-quality printing needs, such as commercial printing and short-run printing |
| Durability | Generally high | Lower |
| Production Efficiency | High | Low |
3. What is the Difference Between Thermal CTP and Violet CTP?
| Feature | Thermal CTP | Violet CTP |
| Exposure Method | Uses infrared laser | Uses violet laser |
| Stability | High stability | Good stability |
| Resolution | High resolution | Lower resolution |
| Durability | High durability | Lower durability |
| Production Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application Scenarios | Long-run printing needs, such as commercial printing and high-quality publishing | Short-run printing needs, such as small-scale publishing and fast printing |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Image Quality | Excellent | Good, though may be slightly lower than thermal CTP |
4. How to Make a CTP Plate?
The following PS and CTP plate may interest you
Further reading: ctp plates for offset printingctp offset machinectp offset printingctp offset printing platesoffset ctpoffset printing ctp plateoffset printing plate making machine