CTP Plate
CTP Plate is a key component in modern offset printing, enabling direct digital imaging from computer files onto printing plates.
CTP Plate is at the core of digital prepress for offset printing. CTP plate systems use various laser technologies to directly transfer digital images onto specially coated aluminum plates, eliminating many traditional bottlenecks. This enhances image quality, shortens production time, reduces costs, and provides a more sustainable printing solution. This technology has become indispensable in modern commercial printing, meeting evolving demands for speed, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
CTP Plate represents the pinnacle of digital imaging technology directly applied to plate making in modern offset printing. Essentially, it transfers digital images directly onto aluminum plates coated with a photosensitive emulsion, eliminating the need for intermediate film production. This process improves overall print quality, shortens turnaround times, lowers production costs, and minimizes the use of chemicals.
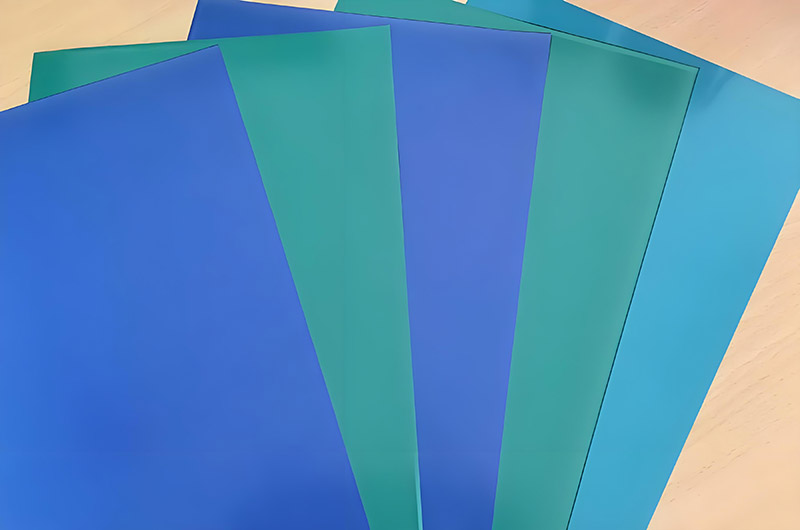

Components of a CTP Plate
|
Component
|
Description
|
|
Substrate
|
The substrate of a CTP Plate is typically made of aluminum or polyester material. Aluminum substrates are widely used in commercial and industrial printing due to their excellent durability and lightweight properties. The surface of the aluminum substrate undergoes electrochemical graining to form a fine porous structure, which enhances water retention and improves the adhesion of the photosensitive coating, ensuring imaging quality. For short-run printing applications, polyester substrates may also be used for CTP Plates, offering lower costs and good flexibility, making them suitable for small-batch production.
|
|
Photosensitive Coating
|
The photosensitive coating of a CTP Plate consists of a layer of polymer or emulsion that reacts to laser exposure, such as photopolymer, silver halide, or thermal coating. Photopolymer coatings cure and form an image under UV or violet laser exposure, while thermal coatings undergo physical or chemical changes under high-energy laser exposure to present the image. The photosensitive coating determines the imaging method, resolution, and exposure speed of the CTP Plate, directly affecting the clarity and color reproduction of the final print.
|
|
Protective Layer
|
The protective layer of a CTP Plate is a thin, transparent coating primarily used to prevent scratches, oxidation, and other physical damage. During handling, storage, and transportation, the protective layer ensures the integrity of the photosensitive coating, preventing performance degradation caused by environmental factors. Additionally, the protective layer has certain moisture and chemical corrosion resistance properties, further extending the storage life of the CTP Plate and ensuring consistent quality before printing.
|
Types of CTP Plates
Different Types of CTP Plates
|
Type
|
CTP Plate Image
|
Description
|
|
Thermal CTP Plate
|

|
Thermal CTP Plates are sensitive to infrared laser energy. They are known for their high durability and excellent dot reproduction, making them frequently used in high-volume printing environments. Thermal plates come in single-layer and double-layer formats, with double-layer designs providing enhanced print stability and image quality.
|
|
Violet CTP Plate
|

|
Violet CTP Plates are imaged using violet laser technology. They are generally more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Although the image resolution may be slightly lower compared to thermal plates, violet plates require fewer chemicals, making them suitable for small to medium-sized printing businesses and cost-sensitive applications.
|
|
Process-Free CTP Plate
|
|
Process-free plates eliminate the chemical development stage. During printing, the non-image areas are removed, reducing waste and operating costs. The image is directly presented on the plate and cleaned by the printing press, minimizing chemical waste and simplifying workflows. This type of plate is ideal for environmentally conscious printing companies seeking simplified production processes.
|
|
Positive and Negative Working Plates
|

|
Positive plates dissolve upon exposure, mainly used for UV imaging plates, where exposed areas become blank. Negative plates harden upon exposure, commonly found in thermal plates, where exposed areas form the image. The choice between positive and negative working plates depends on the printing application, imaging method, and printing press compatibility.
|
Comparison of Different Types of CTP Plates
|
Parameter
|
Thermal CTP Plate
|
Photopolymer CTP Plate
|
Process-Free CTP Plate
|
|
Laser Type
|
Infrared Laser (830 nm)
|
Violet Laser (405 nm)
|
Infrared/Violet Laser
|
|
Development Process
|
Chemical Development (Some Require Baking)
|
Alkaline Developer
|
No Development Required
|
|
Print Run Durability
|
100, 000+ Impressions
|
50, 000-80, 000 Impressions
|
30, 000-50, 000 Impressions
|
|
Resolution
|
2400-2540 dpi
|
2400-3000 dpi
|
2400 dpi
|
|
Environmental Impact
|
Medium (Requires Chemical Processing)
|
Medium (Requires Developer)
|
High (Zero Chemical Emissions)
|
|
Cost
|
High (Equipment + Consumables)
|
Medium
|
Medium to High (Higher Plate Cost)
|
|
Application Scenarios
|
Long Runs, High-Precision Printing
|
Medium to Short Runs, Fine Graphics
|
Short Runs, Eco-Friendly Printing
|
How to Choose a CTP Plate?
-
Choose Thermal CTP for Long Runs: Ideal for high durability and stability (e.g., packaging boxes, textbooks).
-
Choose Photopolymer CTP for High-Precision Printing: Best for fine image reproduction (e.g., art books, luxury packaging).
-
Choose Process-Free CTP for Eco-Friendly Needs: Suitable for meeting regulations or short-run quick printing (e.g., food labels, corporate brochures).
The selection of CTP plates requires balancing factors like print volume, resolution needs, environmental considerations, and budget constraints. Thermal plates are known for their durability, photopolymer plates excel in high-resolution applications, and process-free plates lead the trend of sustainable printing.
Advantages of CTP Plate Technology
|
Advantages
|
Description
|
|
Enhanced Image Quality
|
By eliminating the intermediate film step, CTP plates provide clearer and more consistent images. The direct imaging technology reduces potential image degradation, enabling the plates to reproduce finer details and achieve smoother color transitions. Additionally, improved registration accuracy reduces color shifts and misregistration errors, enhancing overall print quality.
|
|
Faster Turnaround
|
CTP plates use a direct imaging method, eliminating the need for film output and exposure steps, significantly reducing processing time. This streamlined plate-making process shortens overall production time, boosting printing line efficiency and providing a faster turnaround, especially beneficial for urgent or short-term tasks.
|
|
Cost-Effectiveness
|
CTP plates eliminate the need for film and related chemicals, reducing material costs and minimizing reliance on film processing equipment. Additionally, the simplified workflow reduces labor requirements, lowering operational costs. For printing companies, CTP technology serves as a long-term cost-saving solution.
|
|
Environmental Benefits
|
With the use of environmentally friendly technologies such as process-free plates and violet CTP plates, the need for chemicals is significantly reduced. By eliminating traditional developing chemicals, CTP plates minimize waste generation and lower the volume of hazardous waste, helping printing companies achieve sustainable production goals.
|
|
Improved Consistency and Registration
|
CTP technology, with its digital control, ensures image accuracy and consistency. During the color separation process, each color can be precisely calibrated using computer technology, resulting in accurate registration. This high level of image consistency is particularly crucial for long-run and high-precision printing.
|
How CTP Plates Work
|
Steps
|
Description
|
|
Digital File Preparation
|
CTP plates work from digital files prepared using desktop publishing software, typically in PDF format. These digital files contain complete image, text, and layout information. The CTP plate receives raster image data converted by the Raster Image Processor (RIP), ensuring the image data is accurately converted into a bitmap format for imaging.
|
|
Laser Imaging
|
CTP plates undergo laser imaging in dedicated plate-making machines. The machine uses laser diodes or UV light to directly expose the photosensitive coating on the CTP plate. Depending on the plate type, the imaging methods include:
-
Thermal Imaging: CTP plates use infrared lasers and thermal-sensitive coatings to create images. This method offers high durability, making it ideal for long-run printing.
-
Violet Laser Imaging: CTP plates use violet lasers for exposure, often chosen for their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly properties, especially for short to medium-run printing.
-
Process-Free Plates: In some systems, CTP plates directly undergo exposure without any chemical processing, simplifying workflows and reducing environmental impact.
|
|
Development (If Required)
|
In traditional development processes, CTP plates go through chemical developers to remove unexposed coating areas, leaving behind clear image regions. After development, the plates are cleaned and stabilized to ensure image durability and accuracy. For process-free plates, the plate’s non-image areas are automatically cleaned during the printing process using the press’s dampening system, achieving chemical-free and eco-friendly plate-making.
|
|
Plate Installation
|
Once imaging and development are complete, the CTP plate is mounted onto the printing press’s plate cylinder. The image areas on the CTP plate attract ink, while the non-image areas repel it. During the printing process, the CTP plate precisely transfers ink onto the substrate (usually paper). The high imaging accuracy and digital control of CTP plates ensure excellent image reproduction, color accuracy, and precise registration.
|
CTP Plate Applications and Considerations
What Printing Scenarios Are Suitable for CTP Plates?
-
Commercial Printing: Magazines, brochures.
-
Packaging: Large-volume cartons and labels.
-
Newspapers: Fast plate-making for daily publications.
-
Short-Run Digital Printing: Polyester plates for quick jobs.

What Should Be Noted When Using CTP Plates?
|
Category
|
Precautions
|
|
Preparation Before Use
|
Environmental Control:
|
|
Temperature and Humidity: The recommended storage and operating temperature is 18-25°C, with humidity at 40-60%. Avoid moisture absorption or cracking of the coating.
|
|
Light Protection: Photopolymer CTP plates should be handled under yellow safety lights, while thermal plates can be processed in a daylight environment.
|
|
Equipment Calibration:
|
|
Regularly calibrate the laser energy and focal distance of the plate setter to ensure dot accuracy within ±1% error.
|
|
Check the developer concentration and temperature (e.g., thermal plate developer typically requires 23-28°C).
|
|
Plate Making Operation Guidelines
|
Exposure Parameters:
|
|
Adjust laser energy according to the plate type (e.g., thermal plates commonly use 200-300 mJ/cm², photopolymer plates use 100-150 μJ/cm²).
|
|
Avoid overexposure, which can cause dot enlargement or coating ablation.
|
|
Development Process:
|
|
Chemical development plates require strict control of the development time (typically 20-40 seconds). Overdevelopment reduces the plate's durability.
|
|
For process-free plates, wipe the surface gently with a soft cloth to remove dust before printing.
|
|
Printing Press Compatibility
|
Ink and Water Balance:
|
|
Process-free plates are sensitive to fountain solution pH (recommended pH 4.8-5.5) and should be checked regularly.
|
|
When using UV inks, ensure that the thermal plate's coating is UV ink-resistant.
|
|
Pressure Adjustment:
|
|
Maintain the pressure between the blanket and plate at 0.1-0.15 mm to avoid surface damage from friction.
|
How to Maintain and Care for CTP Plates?
|
Category
|
Maintenance and Care Measures
|
|
Daily Cleaning
|
Post-Printing Cleaning:
|
|
Use a neutral detergent (pH 6-8) and a non-woven cloth to wipe the plate surface, removing ink residues.
|
|
Avoid using strong acidic/alkaline solvents or steel wool to prevent coating scratches.
|
|
Equipment Maintenance:
|
|
Clean the plate setter’s optical lens weekly with anhydrous ethanol to prevent dust from affecting imaging accuracy.
|
|
Storage Guidelines
|
Unexposed Plates:
|
|
Aluminum Base Plates: Store vertically in a cool, dry place to prevent deformation from stacking.
|
|
Polyester Base Plates: Store flat to prevent bending. Shelf life is typically 12-18 months.
|
|
Exposed but Not Developed Plates:
|
|
Thermal plates should be developed within 24 hours, while photopolymer plates should be developed within 48 hours to prevent latent image degradation.
|
|
Lifespan Extension Tips
|
Baking Treatment:
|
|
After development, thermal plates can be baked at 220-250°C for 5-8 minutes to increase durability by 30%-50%.
|
|
Fountain Solution Management:
|
|
Regularly replace the fountain solution (recommended every 2000 prints) to prevent impurities from accumulating and damaging the plate surface.
|
Common Issues and Solutions for CTP Plate
|
Issue
|
Possible Cause
|
Solution
|
|
Blurry Print Dots
|
Insufficient Laser Energy / Focus Deviation
|
Recalibrate the plate-making machine and check the laser head status
|
|
Plate Surface Dirty
|
Incomplete Developing / Abnormal Fountain Solution pH
|
Extend developing time or replace the developer; Adjust the fountain solution
|
|
Abrupt Decrease in Plate Durability
|
Insufficient Baking / Excessive Printing Pressure
|
Perform proper baking as per guidelines; Adjust the printing press pressure
|
|
Non-Treatment Plate Not Accepting Ink
|
Residual Protective Film Not Removed
|
Pre-treat the plate surface using water or a dedicated cleaner
|
Proper use and maintenance of CTP plates can significantly enhance printing efficiency, reduce costs, and extend the plate’s lifespan. Pay attention to environmental control, equipment calibration, and development standards. Routine maintenance and rapid troubleshooting according to the plate type (thermal, photopolymer, or process-free) ensure stable and reliable print quality.
Comparison Between CTP Plate and Other Technologies
What are the Differences Between CTP Plate and PS Plate?
|
Comparison Dimension
|
CTP Plate (Computer-to-Plate)
|
PS Plate (Pre-sensitized Plate)
|
|
Plate-Making Process
|
Direct imaging from digital files using laser, without the need for film
|
Film output required first, followed by UV exposure to transfer the image to the PS plate
|
|
Imaging Precision
|
High resolution (2400-3000 dpi) with dot error ±1%
|
Limited by film quality (typically 1200-2400 dpi) with higher error margins
|
|
Production Efficiency
|
Eliminates the film step, increasing plate-making speed by 50% or more
|
Requires film developing, plate exposing, and additional steps, making it time-consuming
|
|
Environmental Impact
|
Reduces chemical waste, especially with process-free CTP plates
|
Film development produces silver-containing wastewater, leading to higher pollution risk
|
|
Cost
|
Higher initial equipment investment but lower long-term costs due to film and labor savings
|
Lower initial investment, but higher operational costs due to continuous film use
|
|
Plate Durability
|
Thermal CTP plates can endure 100, 000+ impressions
|
Standard PS plates typically last 50, 000-80, 000 impressions
|
|
Application Scenarios
|
Suitable for medium to long-run printing with high precision (e.g., packaging, commercial printing)
|
Suitable for short-run printing with low budget requirements (e.g., flyers, business cards)
|
Comparison Between CTP Technology and Other Plate-Making Technologies
|
Comparison Item
|
CTP
|
CTF (Computer-to-Film)
|
Digital Printing (Laser/Inkjets)
|
|
Technical Principle
|
Fully digital laser imaging, automated operation
|
First output film, then expose it to the PS plate
|
Directly print on paper or materials
|
|
Accuracy and Consistency
|
High accuracy, strong consistency, no human errors
|
Film quality affects accuracy, risk of defects
|
General accuracy, depends on equipment performance
|
|
Cost
|
High initial equipment investment, low plate cost
|
Film cost accounts for 15%-20% of total cost
|
No plate making required, low short-run cost
|
|
Efficiency
|
Automated plate making, high efficiency
|
Film making and plate exposure are time-consuming
|
Instant printing, no waiting required
|
|
Environmental Friendliness
|
Environmentally friendly, no film development waste
|
Film development waste contains silver and chemicals
|
No chemical processing required, minimal environmental impact
|
|
Applicable Scenarios
|
Medium to long-run printing, suitable for high-quality offset printing
|
Still used in traditional printing plants
|
Personalized customization, ultra-short-run printing
|
|
Economic Threshold
|
More cost-effective for 500-1000 copies and above
|
Not economical for less than 500 copies
|
Short-run cost-effective for 1-500 copies
|
Why Choose CTP Technology?
|
Advantage Category
|
Specific Advantage
|
|
Efficiency and Cost Advantage
|
Shortens delivery cycle: Reduces plate-making time by 30%-50%.
|
|
Saves on film, chemicals, and storage costs.
|
|
Improved Printing Quality
|
Supports screen rulings of 300 lines/inch or higher, accurately reproduces gradients and fine text.
|
|
Digital control ensures batch consistency.
|
|
Environmental Compliance
|
No development waste for process-free CTP plates, compliant with environmental regulations.
|
|
Aluminum-based plates can be recycled, reducing carbon footprint.
|
|
Adaptation to Industry Trends
|
Strong ability for quick job changes, plate-making completed within 30 minutes.
|
|
Can be integrated with MIS and color management software for intelligent production.
|
CTP Plate Advantages Over Traditional Methods
-
Efficiency: CTP Plate eliminates the need for film, reducing costs and processing time.
-
Quality: Higher resolution (up to 2400+ DPI) and finer screen rulings (200+ lpi), achieving clearer halftones.
-
Accuracy: CTP Plate minimizes errors in the film processing phase.
-
Environmental Impact: Reduces the use of chemicals, especially when using process-free plates.
The following PS and CTP plate may interest you
Further reading: ctp machinectp plate making machinecomputer to plate ctpctp plates for offset printingctp printingctp computerctp computer to platectp computer to plate machinectp machine for printingctp offset machinectp offset printingctp offset printing platesctp plate machinectp printing platectp thermaloffset printing ctp plateplate ctp





